how-safaris-intelligent-tracking-preventionitp-is-blocking-your-google-ads-tags
If you’re running Google Ads campaigns, you might notice something strange: conversions look lower than the backend numbers, and delayed conversions (where a user clicks today but buys after a few days) are not showing up . We are discussing how this impacts your google campaigns ability to convert cold audiences especially when you get a good chunk of traffic from Safari and apple devices.
Why does this happen? Because Safari’s Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) is quietly blocking Google Ads tags from tracking users over time.
Here’s what that means in simple terms:
- Google can’t see the full customer journey on Safari.
- When a user clicks your ad today but buys later, that “delayed conversion” often doesn’t get reported.
- At first, this mainly affects your reports — conversions appear to be missing and attribution sucks.
- But in the long run, Google’s algorithm stops targeting people who take longer to convert, because it doesn’t have data about them.
- This also affects the dynamic remarketing and RLSA abilities of Google Pmax and smart bidding search campaigns .
- As a result, campaigns shift toward only targeting people who are already close to buying — and your google campaigns ability to build awareness or nurture customers disappears.
In this article, we’ll break down what ITP is, how it works in Safari browser, how it affects Google Ads tracking and retargeting, and why this leads to missing conversions, broken retargeting, and disappointing results when budgets are increased. We’ll also share an example from a real client case to make it easier to understand.
What Is Intelligent Tracking Prevention?
Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) is Safari’s built-in privacy guard. Its job is to stop advertisers and websites from following you around the internet using tracking cookies and other techniques.
Think of it as a bouncer at a club — it watches out for “tracking cookies” and throws them out before they’ve been around too long.
Why Apple Created ITP
Apple wants to market Safari as a privacy-first browser. That means limiting “cross-site tracking” — when advertisers track what you do across different websites to show you targeted ads.
By tightening tracking rules, Apple:
- Protects user privacy.
- Differentiates Safari from competitors like Chrome.
- Makes it harder for ad companies like Google and Facebook to collect data freely.
How ITP Works
Websites and advertisers track you using cookies — little files that remember who you are.
There are two main types:- First-party cookies – from the site you are directly visiting.
- Third-party cookies – from other companies’ tools (like Google Ads or Facebook Pixel) loaded on that site.
Here’s what ITP does:
- Blocks third-party cookies completely — they can’t even be set.
- Shortens the life of tracking cookies — if Safari suspects a cookie is for tracking, it can delete it after just 24 hours or a maximum of 7 days.
- Detects and restricts known trackers — uses machine learning to spot tracking patterns and shut them down.
- Prevents fingerprinting — hides or randomizes device details to make you harder to identify.
How This Breaks Google Ads Tracking
Here’s the problem: Google Ads needs cookies to remember that someone clicked your ad before making a purchase.
Example:
- A Safari user clicks your Google Ad.
- They visit your site but don’t buy right away.
- A few days later, they come back and buy.
Without ITP:
The cookie is still there → Google Ads matches the sale to the ad click → You see the conversion in reports.With ITP:
Safari deletes the cookie after 24 hours or 7 days → When they come back, Google Ads doesn’t know they’re the same person → No conversion recorded.Result:
- Your sales might be fine, but conversions from Safari users disappear from your data.
- Google Ads gets fewer “signals” for campaign optimization.
The Hidden Effect on Retargeting & Conversion Lag
Here’s something many advertisers miss: ITP doesn’t just affect reporting — it also affects how Google Ads’ algorithm works.
- Safari deletes the cookie and buyer details → Google can’t “remember” the customer journey.
- That means Google can’t see if someone revisits your site from an earlier click.
- Because of this, retargeting on Safari is nearly impossible. Google simply doesn’t know it’s the same customer returning.
So, the algorithm shifts its focus:
- Instead of guiding people from awareness → consideration → conversion, Google Ads ends up only recognizing people already close to buying (conversion-state customers).
- As a result, your reports show no conversion lag (because Google can’t connect the earlier awareness/consideration clicks).
- And if you increase the budget, it often delivers fewer results — because Google can’t bid to nurture awareness-level audiences (those signals are lost)
Example: A Client Case We Analyzed
We recently worked with a client who increased their ad budget in campaigns designed to build awareness and consideration.
Here’s what happened:
- Traffic increased, mostly from Safari users.
- Reports showed no improvement in conversion lag.
- Final results did not increase much, despite the higher budget.
Why? Because Safari deleted the cookies that would have tracked users from the awareness stage to the conversion stage. Google Ads couldn’t see the full journey, so it optimized only for customers already at the decision point.
To the client, it looked like the budget increase wasn’t working — but the real issue was ITP hiding the middle part of the funnel.
Why This Matters More Than You Think
Safari has a huge share of mobile browsing, especially in iPhone-heavy markets like the UAE, US, and Europe.
If a large chunk of your audience is on iPhones/iPads, ITP can hide a significant portion of your ad performance.What You Can Do About It
While you can’t turn ITP off for users, you can improve tracking accuracy:
- Server-side tagging – move tracking from the browser to your server.
- Enhanced Conversions in Google Ads – uses hashed customer data (like emails) to match conversions even without cookies.
- Shorter retargeting windows – target Safari visitors within 1–7 days.
- CRM integration – feed offline or backend sales data directly into Google Ads.
- GA4 server-side setup – less impacted by ITP restrictions.
Safari’s Intelligent Tracking Prevention is a big privacy win for users — but a challenge for advertisers.
Not only does it hide conversions in reports, but it also breaks retargeting and conversion lag tracking, forcing Google Ads to optimize only for bottom-funnel customers. That’s why budget increases often show smaller-than-expected results.
If you understand how ITP works and adjust your strategy with smarter tracking solutions, you can still get an accurate picture of your campaigns and avoid wasting budget.
Your Google Ads results may not be as bad as the reports suggest — sometimes, the data is just hidden behind Apple’s privacy curtain.


 “This purchase came from this ad click”
“This purchase came from this ad click”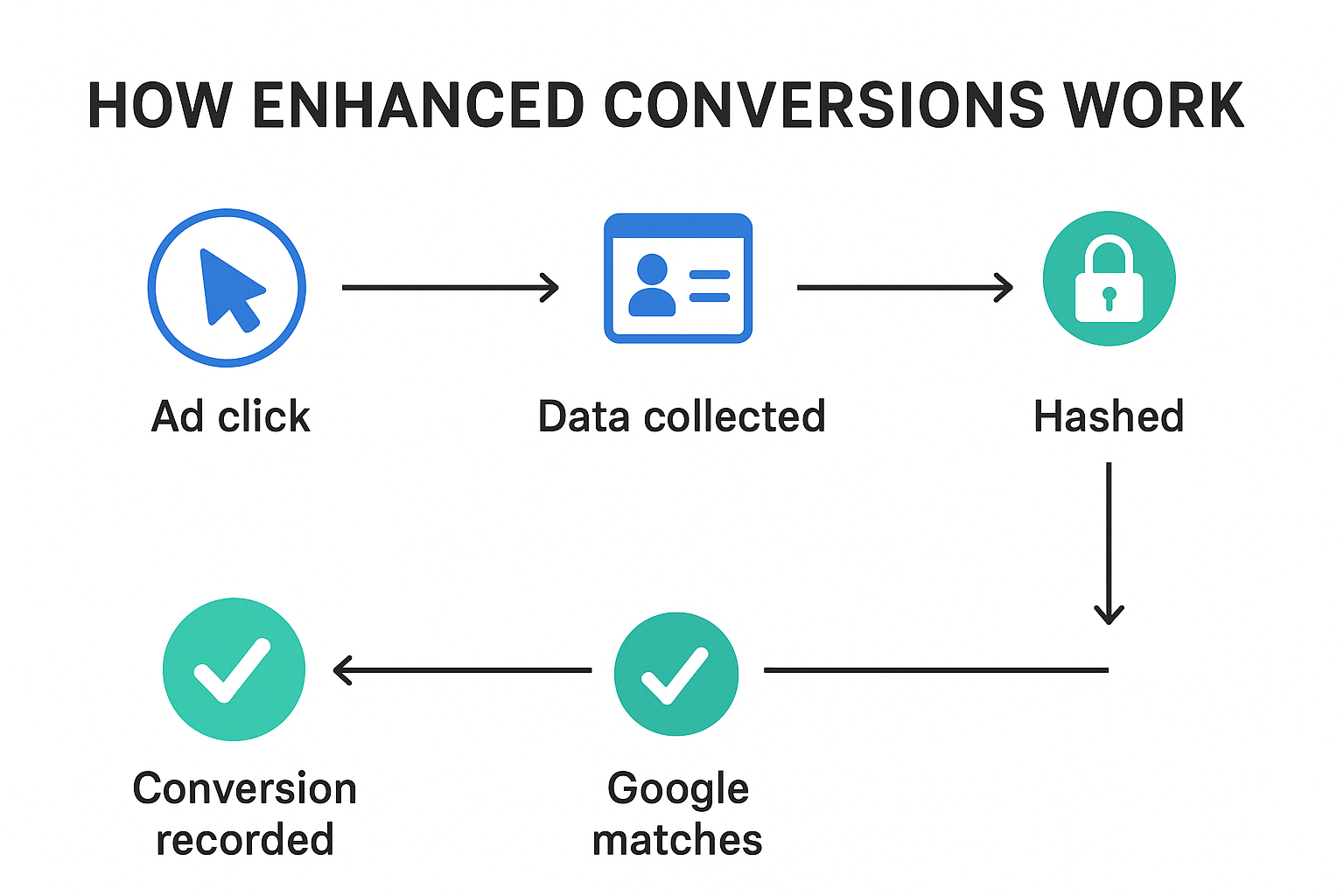
 Take away:
Take away:
 Both strategies rely heavily on cookies and tracking tags to recognize the same user when they come back. And this is where ITP comes in.
Both strategies rely heavily on cookies and tracking tags to recognize the same user when they come back. And this is where ITP comes in. Impact on RLSA (Remarketing Lists for Search Ads)
Impact on RLSA (Remarketing Lists for Search Ads)
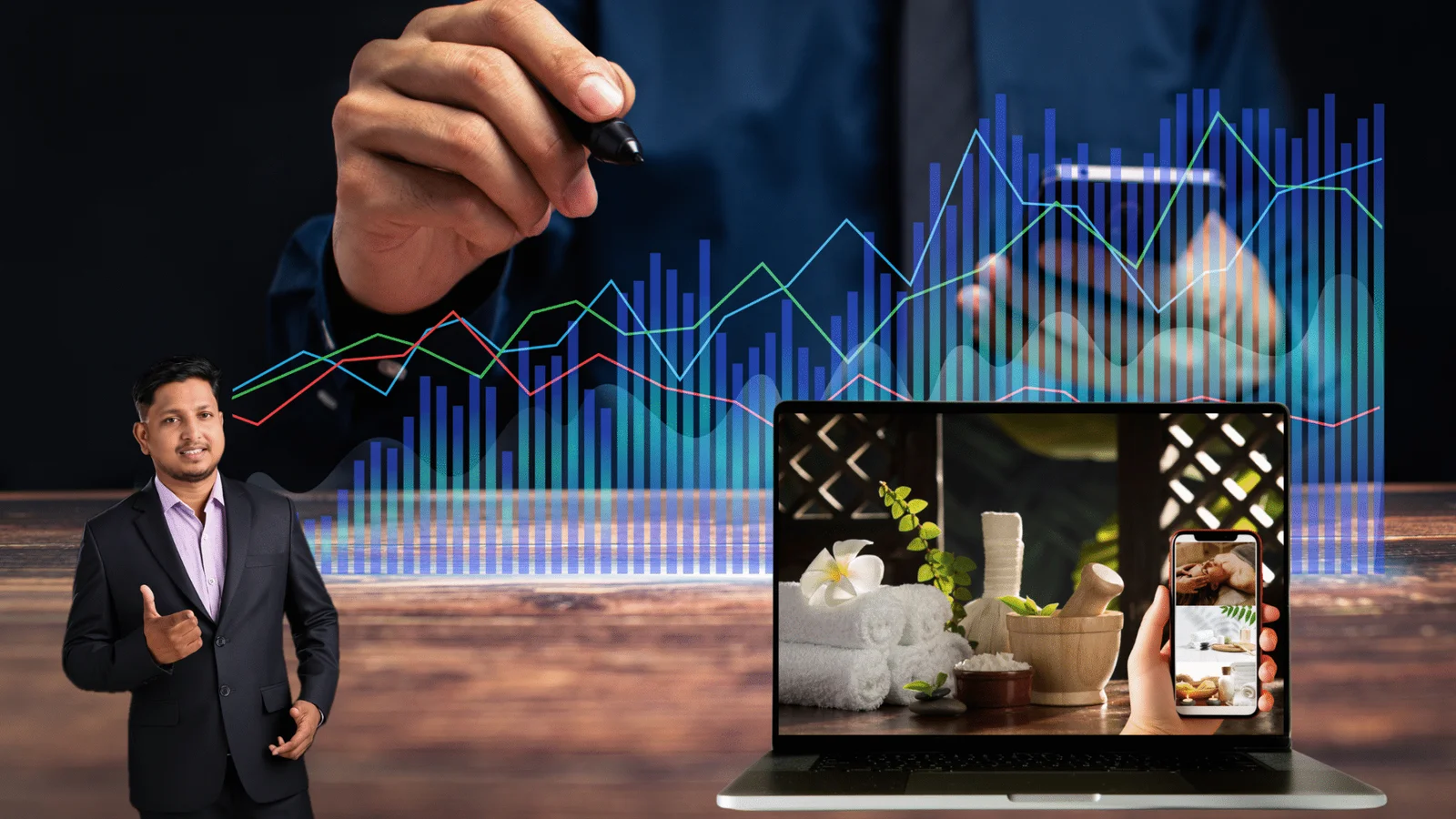
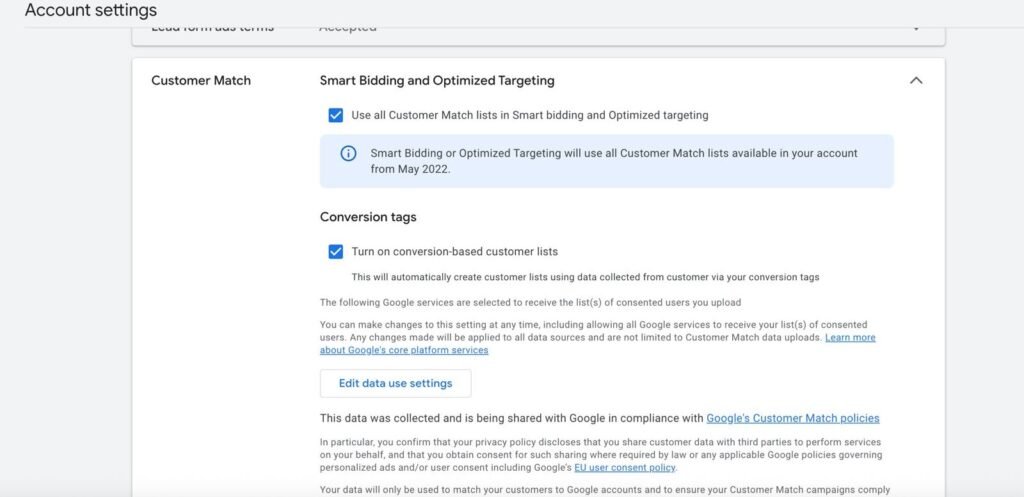

 Challenge
Challenge Segmented campaigns by user intent (new users vs. remarketing)
Segmented campaigns by user intent (new users vs. remarketing) A/B testing multiple landing page variants
A/B testing multiple landing page variants Implemented various Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) pracices in the landing page.
Implemented various Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) pracices in the landing page. The Results
The Results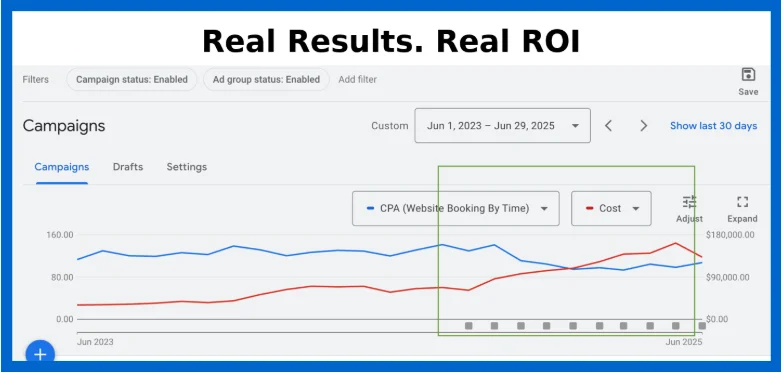
 As shown in the graph below, CPA consistently declined even as budget and bookings increased — delivering exponential ROI.
As shown in the graph below, CPA consistently declined even as budget and bookings increased — delivering exponential ROI. Services Used
Services Used Want results like this?
Want results like this?